Learn how to secure your family’s financial future with these essential tips for creating a sustainable financial plan. From budgeting to investing, discover the key strategies to ensure long-term stability and prosperity for your loved ones.
Importance of Financial Planning

Financial planning is crucial for families of all sizes and income levels. It provides a roadmap to achieve your financial goals, secure your family’s future, and navigate life’s uncertainties. Here’s why financial planning is paramount:
1. Defines and Prioritizes Financial Goals
Financial planning helps you identify and prioritize your family’s short-term and long-term financial goals. These goals may include buying a home, funding your children’s education, securing a comfortable retirement, or leaving a legacy.
2. Creates a Realistic Budget
A well-structured financial plan includes a comprehensive budget that tracks income, expenses, and savings. This allows you to monitor your cash flow, identify areas to reduce spending, and allocate funds effectively.
3. Builds a Strong Financial Foundation
By following a financial plan, you establish a solid financial foundation for your family. This includes building an emergency fund, managing debt responsibly, and establishing good credit.
4. Secures Your Family’s Future
Life is unpredictable. Financial planning helps you prepare for unforeseen events such as job loss, medical emergencies, or disability. Adequate insurance coverage and a robust emergency fund provide a safety net for your loved ones.
5. Achieves Financial Freedom
Ultimately, financial planning empowers you to achieve financial freedom. It allows you to make informed financial decisions, avoid debt traps, and pursue your dreams with confidence.
Setting Financial Goals
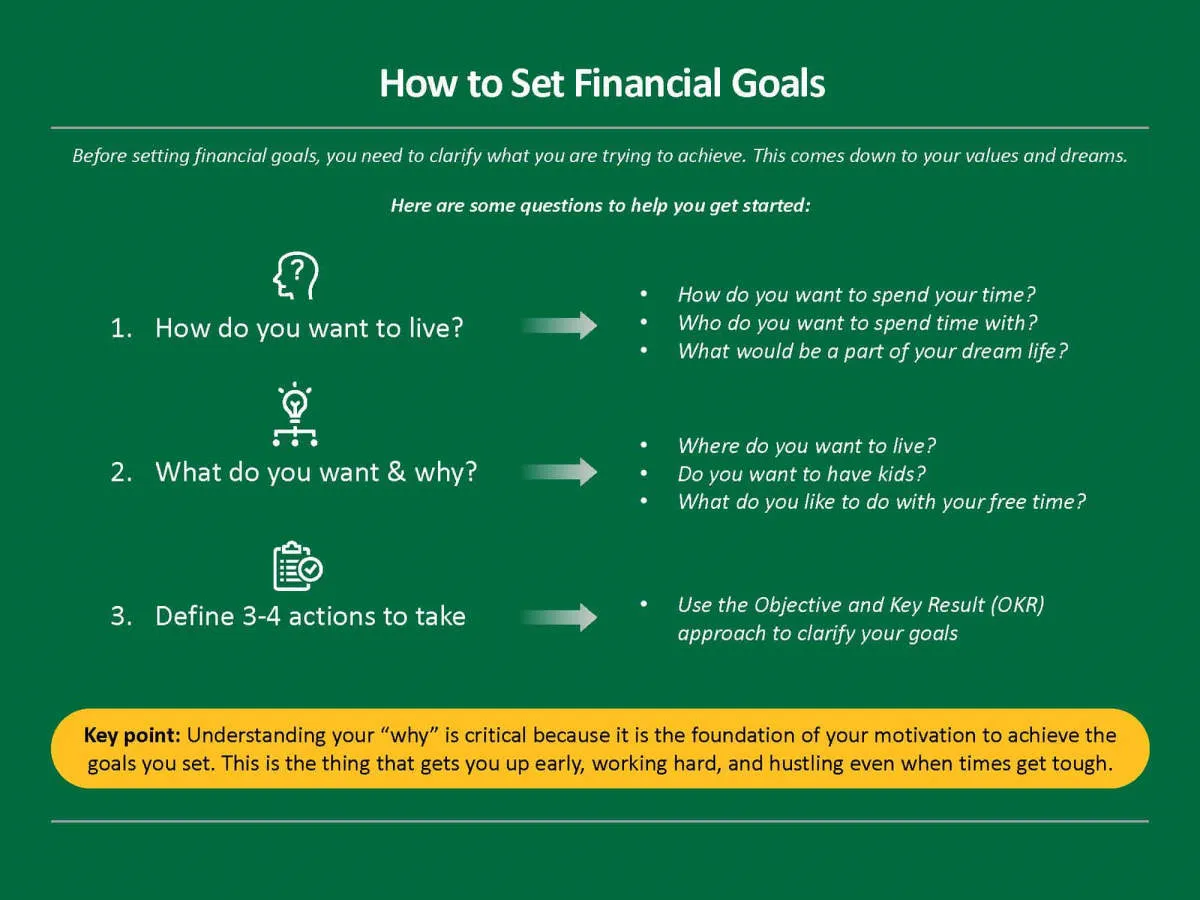
A sustainable financial plan starts with a clear vision of what you want to achieve. Setting financial goals provides direction and motivation, helping you stay focused on building a secure future for your family.
Types of Financial Goals
Financial goals can be categorized by their time horizon:
- Short-term goals are achievable within a year, like building an emergency fund or paying off a credit card.
- Mid-term goals typically span 2 to 5 years, such as saving for a down payment on a house or a family vacation.
- Long-term goals require 5+ years of planning, including retirement planning or funding your children’s education.
Setting SMART Goals
When setting your family’s financial goals, aim for SMART goals:
- Specific: Clearly define your goal, like “Save $10,000 for a down payment.”
- Measurable: Track your progress with quantifiable targets, e.g., “Save $500 per month.”
- Achievable: Set realistic goals considering your income and expenses.
- Relevant: Align your goals with your family’s values and priorities.
- Time-bound: Establish deadlines to create urgency and accountability.
Involving Your Family
Engage your family in discussions about financial goals. Encourage open communication about needs, aspirations, and potential trade-offs. This shared understanding fosters commitment and makes achieving your goals a collective effort.
Creating a Family Budget
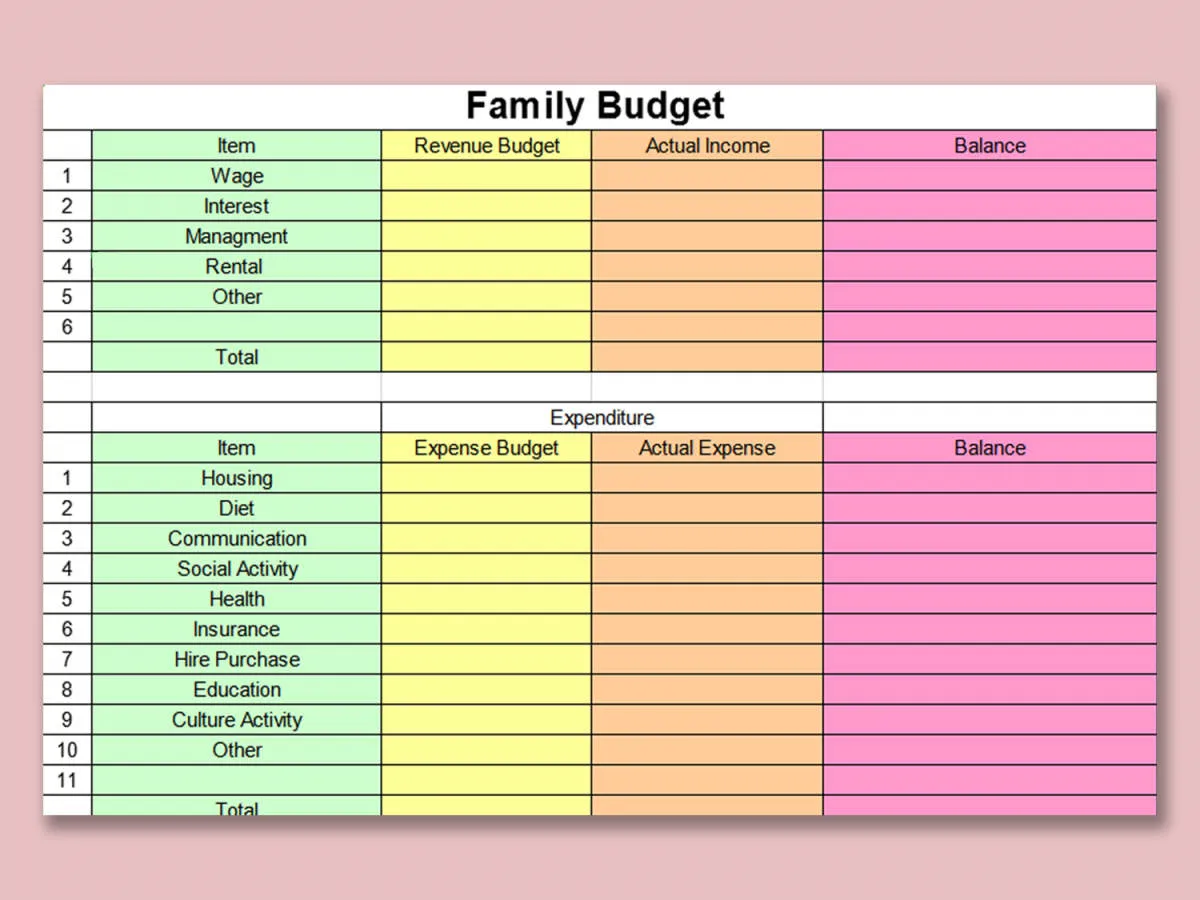
A sustainable financial plan always starts with a well-structured budget. This holds especially true for families, where managing income and expenses across multiple individuals requires careful planning and coordination.
Creating a family budget involves several key steps:
- Track Income and Expenses: Begin by diligently tracking all sources of income and every expense your family incurs. Utilize budgeting apps, spreadsheets, or even a simple notebook to record this information accurately.
- Categorize Spending: Divide your expenses into distinct categories, such as housing, groceries, transportation, utilities, entertainment, and savings. This categorization provides a clearer picture of where your money goes.
- Set Financial Goals: Determine your family’s short-term and long-term financial objectives. Whether it’s saving for a down payment, funding education, or planning for retirement, having clear goals guides your budget allocation.
- Allocate Funds: Based on your income, expenses, and financial goals, allocate specific amounts to each spending category. Prioritize essential expenses and allocate funds strategically to align with your goals.
- Review and Adjust Regularly: Life is dynamic, and your financial situation may change over time. Regularly review your budget, ideally on a monthly basis, and make adjustments as needed to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
By establishing a comprehensive family budget and adhering to its principles, you lay the foundation for a more secure and sustainable financial future for your loved ones.
Saving for Future Expenses

Creating a sustainable financial plan isn’t just about managing today’s expenses; it’s about securing your family’s future. A crucial part of this is proactively saving for known future expenses and building a safety net for the unexpected.
Identify Future Expenses:
Start by listing down significant anticipated expenses. This could include:
- Education: College funds for your children
- Housing: Down payment for a new home or renovations
- Retirement: Ensuring a comfortable life after work
- Healthcare: Covering potential medical costs
- Family Events: Weddings, milestone celebrations, etc.
Estimate Costs and Timeline:
Research the potential cost of each expense and estimate when you might need the funds. Online calculators can be helpful for this purpose. For longer-term goals like retirement, factor in inflation to ensure you’re saving enough.
Set Savings Goals and Strategies:
Break down each large expense into smaller, manageable savings goals. Decide on a regular saving amount and frequency that fits comfortably within your budget. Consider automating these savings transfers to stay consistent.
Explore Savings and Investment Options:
Depending on your timeline and risk tolerance, explore different options like:
- High-yield savings accounts: For short-term goals, these offer better interest rates than regular savings accounts.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): These offer fixed interest rates over a set period, providing predictable returns.
- 529 Plans: Specifically designed for education savings with tax advantages.
- Retirement Accounts (401k, IRA): Offer tax benefits and long-term growth potential for retirement.
Emergency Fund:
While planning for specific expenses, don’t forget the importance of a robust emergency fund. Aim to save 3-6 months’ worth of living expenses to cover unexpected events like job loss or medical emergencies.
Investing for Long-Term Growth
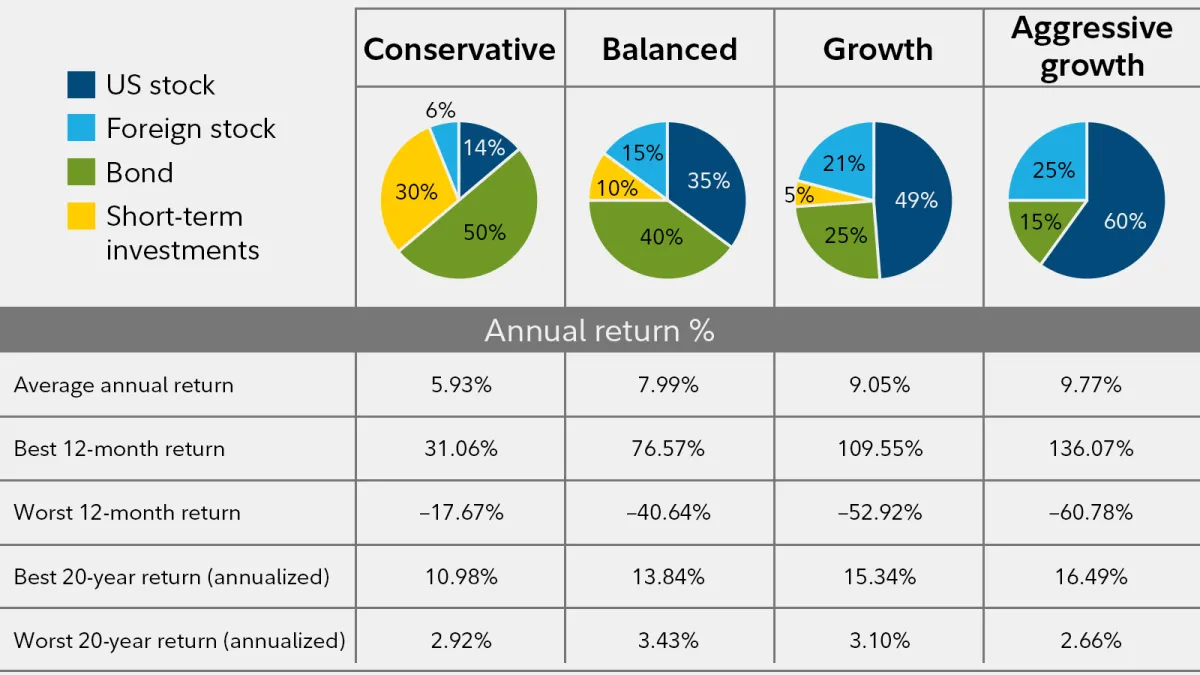
Creating a sustainable financial plan for your family isn’t just about paying the bills today; it’s about building a secure future. A key element of this is investing for long-term growth. This approach focuses on building wealth gradually over time, allowing you to achieve major financial goals like a comfortable retirement or your children’s education.
Here are some important considerations for long-term investment growth:
1. Start Early and Be Consistent
The magic of compounding means your money has more time to grow the earlier you start. Even small, consistent contributions can make a big difference over time. Don’t be discouraged by small beginnings; the key is to start as soon as possible.
2. Diversify Your Portfolio
Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Diversifying your investments across different asset classes like stocks, bonds, and real estate can help mitigate risk. This strategy helps protect you from significant losses if one area of the market underperforms.
3. Consider Your Risk Tolerance
Investing always involves some degree of risk. Your risk tolerance—how comfortable you are with potential market fluctuations—will determine the right mix of investments for you. Generally, younger investors with a longer time horizon can afford to take on more risk than those nearing retirement.
4. Explore Tax-Advantaged Accounts
Take advantage of tax-advantaged accounts like 401(k)s and IRAs. These accounts can help you save for retirement in a tax-efficient manner, maximizing your returns over the long run.
5. Seek Professional Guidance
Navigating the world of investing can feel overwhelming. Don’t hesitate to consult with a qualified financial advisor. They can provide personalized advice, help you build a diversified portfolio aligned with your goals, and adjust your strategy as needed over time.
Reviewing and Adjusting Your Plan

Creating a financial plan isn’t a “set it and forget it” kind of task. Life is dynamic, throwing unexpected curveballs that can impact your finances. That’s why regularly reviewing and adjusting your plan is crucial for its long-term success.
How Often Should You Review?
Aim for at least an annual review of your financial plan. However, certain life events might necessitate more frequent check-ins. These events can include:
- Marriage or divorce
- Birth or adoption of a child
- Job loss or significant income change
- Major unexpected expenses (medical bills, home repairs)
- Receiving an inheritance or large financial windfall
What to Focus On During Your Review
During your review, consider these key areas:
- Goal Assessment: Are you on track to meet your short-term and long-term financial goals? Have any of your goals changed?
- Budget Evaluation: Review your income and expenses. Identify areas where you can reduce spending or explore opportunities to boost your income.
- Debt Management: Assess your progress on paying down debt. Are your debt reduction strategies effective? Do you need to explore other options?
- Investment Performance: Evaluate the performance of your investment portfolio. Are your investments aligned with your risk tolerance and financial goals?
- Emergency Fund: Is your emergency fund sufficient to cover 3-6 months of living expenses? Do you need to replenish it due to recent unexpected costs?
- Insurance Coverage: Review your insurance policies (health, life, property) to ensure you have adequate coverage for your family’s needs.
Making Adjustments
Based on your review, don’t hesitate to make necessary adjustments to your financial plan. This might involve:
- Modifying your budget
- Re-allocating investments
- Adjusting savings contributions
- Exploring debt consolidation options
- Updating your insurance coverage
Conclusion
In conclusion, creating a sustainable financial plan for your family is crucial for long-term stability and security. By following these tips, you can build a strong financial foundation that will support your family’s future needs.