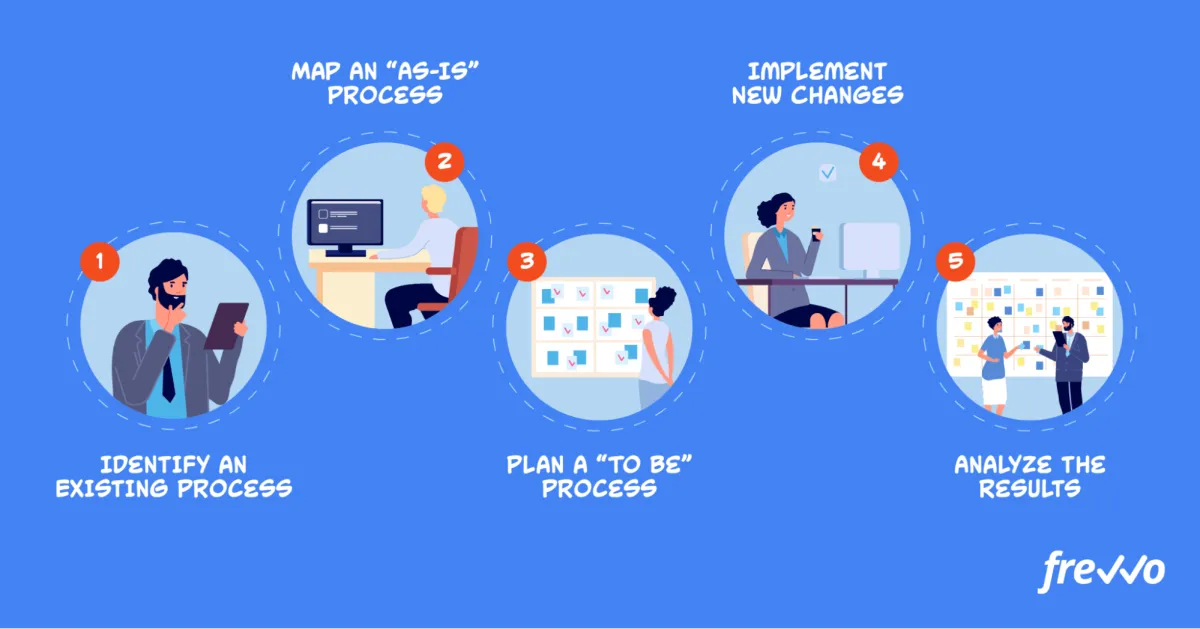
Learn how to enhance your company’s productivity and profitability by implementing effective process optimization strategies in our article on Maximizing Business Efficiency Through Process Optimization.
Understanding Process Optimization
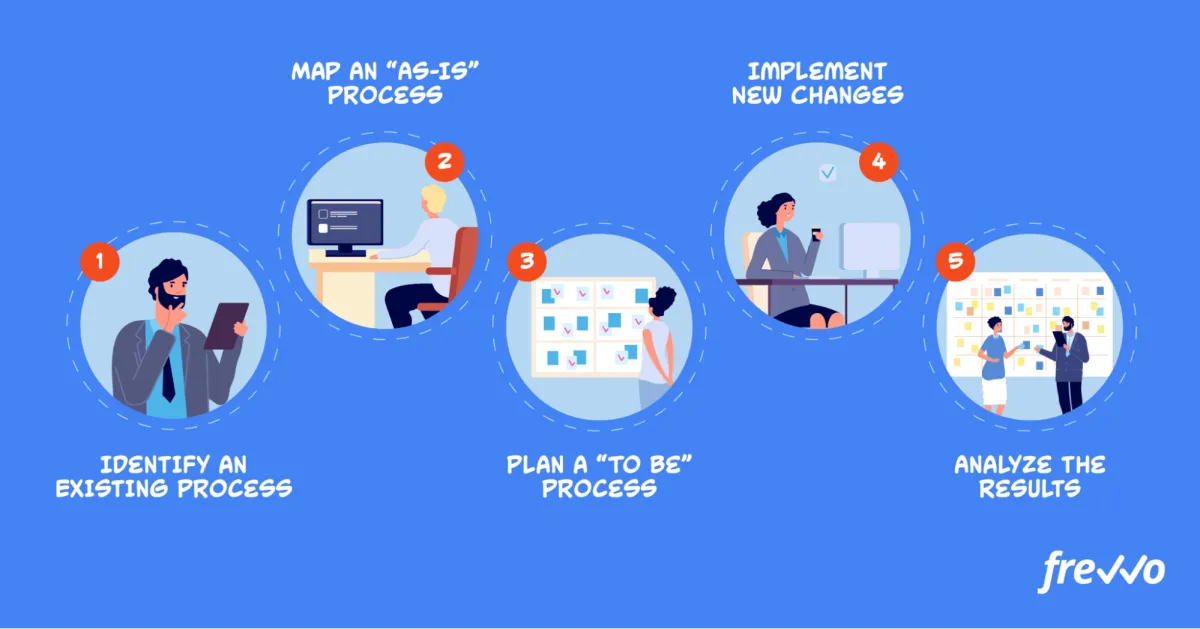
Process optimization is the systematic approach to identifying, analyzing, and refining existing business processes to enhance efficiency and achieve better outcomes. It goes beyond simply identifying bottlenecks; it involves understanding the intricate details of how work flows, where redundancies exist, and how to streamline operations for maximum productivity.
Key aspects of process optimization include:
- Process Mapping: Visually representing each step of a process to understand its flow and identify areas for improvement.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering relevant data to measure key performance indicators (KPIs) and pinpoint areas of inefficiency.
- Identifying Bottlenecks and Inefficiencies: Analyzing data and process maps to locate steps that slow down the overall workflow or create unnecessary work.
- Redesigning and Streamlining: Implementing changes to eliminate bottlenecks, reduce redundancy, and optimize resource allocation.
- Automation: Introducing technology solutions to automate repetitive or time-consuming tasks, freeing up human resources for higher-value activities.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Regularly evaluating the effectiveness of implemented changes and making further adjustments as needed to ensure ongoing optimization.
Identifying Inefficiencies

Before any optimization can take place, you need to pinpoint exactly where your business processes are falling short. This requires a thorough and objective analysis of your current operations.
Here are a few key areas to focus on when identifying inefficiencies:
1. Bottlenecks
Bottlenecks are points in your process where work piles up, slowing down the entire workflow. Look for areas with consistent backlogs, delays, or reduced output.
2. Redundancies
Redundancies occur when the same task is performed multiple times, often unnecessarily. Identify tasks that seem superfluous, are duplicated across departments, or could be consolidated.
3. Manual Processes
While not all manual processes are inefficient, they are often prime candidates for automation. Evaluate manual tasks for their time consumption, error rates, and potential for automation.
4. Data Silos
When information is isolated in different departments or systems, it hinders collaboration and slows down decision-making. Identify where communication breakdowns occur and where data is not readily accessible.
5. Employee Feedback
Your employees are on the front lines of your business processes. Gather their insights and feedback on pain points, areas for improvement, and potential solutions they’ve identified.
Utilizing data analysis tools, process mapping techniques, and conducting comprehensive employee interviews can provide valuable insights into these areas of inefficiency.
Implementing Process Improvements
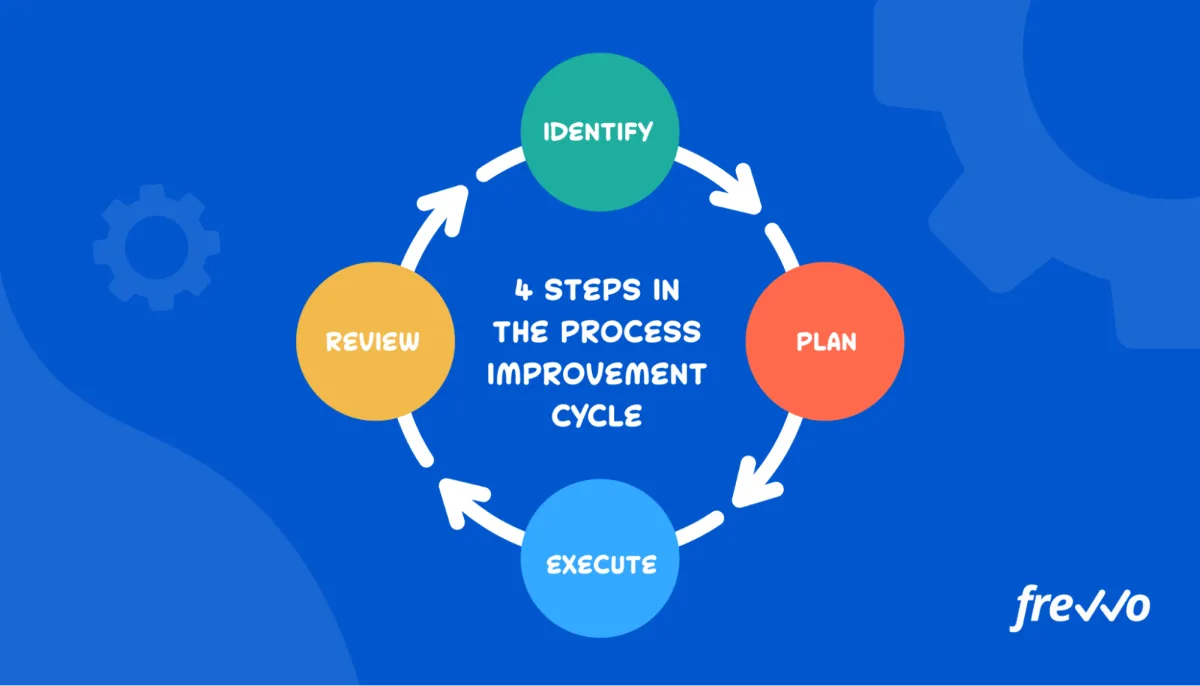
Once you’ve analyzed your processes and identified areas for improvement, it’s time to put those changes into action. This stage requires careful planning and execution to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the chances of success. Here’s a breakdown of key steps involved:
1. Prioritize and Sequence Improvements:
Don’t try to tackle everything at once. Prioritize improvements based on their potential impact and feasibility. Consider factors like resource availability, project complexity, and potential disruption to operations. Create a clear roadmap that outlines the sequence of implementation, taking dependencies into account.
2. Design and Document New Processes:
Clearly define the new or modified processes, outlining each step, responsible parties, and expected outcomes. Use process mapping tools or flowcharts to visually represent the workflow. Detailed documentation ensures everyone understands the changes and facilitates training.
3. Communicate Effectively:
Transparent communication is crucial throughout the implementation phase. Clearly communicate the rationale behind the changes, the expected benefits, and the impact on different stakeholders. Address concerns, provide regular updates, and actively solicit feedback to ensure buy-in and smooth adoption.
4. Provide Adequate Training:
Equip your team with the necessary skills and knowledge to successfully adopt the new processes. Training programs should be tailored to different roles and responsibilities, focusing on practical application and addressing potential challenges. Ongoing support and resources should be available to reinforce learning and provide assistance when needed.
5. Test and Pilot:
Before rolling out changes organization-wide, consider implementing a pilot phase within a smaller, controlled environment. This allows you to test the effectiveness of the new processes, identify potential issues, and gather valuable feedback for further refinement. It also minimizes disruption and allows for adjustments before full-scale deployment.
6. Monitor and Measure:
Implementing process improvements is an iterative process. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the impact of the changes. Regularly monitor these metrics, analyze the results, and make necessary adjustments to optimize the processes further. Continuous improvement should be an ongoing goal.
Using Technology for Efficiency

Technology plays a crucial role in boosting business efficiency through process optimization. By leveraging the right tools and software, organizations can streamline workflows, automate tasks, and improve overall productivity. Here are some key ways technology can be utilized:
1. Workflow Automation:
Automation tools can eliminate manual and repetitive tasks, freeing up employees’ time for more strategic initiatives. From data entry and invoice processing to email marketing and social media management, numerous processes can be automated, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
2. Data Analytics and Reporting:
Data analytics platforms provide businesses with valuable insights into their operations, enabling them to identify bottlenecks, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and make data-driven decisions to optimize processes. Real-time reporting and dashboards offer a comprehensive view of business performance, facilitating timely adjustments and improvements.
3. Communication and Collaboration Tools:
Effective communication and collaboration are vital for efficient business operations. Project management software, instant messaging applications, and video conferencing tools facilitate seamless communication among team members, improving coordination and reducing delays.
4. Cloud Computing:
Cloud-based solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. By migrating processes to the cloud, businesses can access resources on demand, reduce IT infrastructure costs, and enhance accessibility for remote teams.
Training Employees

Process optimization often involves changes to existing workflows, the introduction of new technologies, and the adoption of different methodologies. To ensure these changes are successful, it’s crucial to invest in comprehensive employee training.
Effective training programs should focus on:
- Understanding the ‘Why’: Clearly communicate the reasons behind the process optimization initiative. Help employees understand how the changes benefit them and the organization as a whole.
- Detailed Process Education: Provide a thorough walkthrough of the new or optimized processes. Use a variety of training methods, such as demonstrations, simulations, and hands-on exercises, to cater to different learning styles.
- Technology Familiarization: If new software or tools are being implemented, dedicate time for employees to become comfortable using them. Offer practical exercises and readily available support to address any technical challenges.
- Change Management: Recognize that change can be met with resistance. Incorporate change management principles into the training to help employees adapt and embrace the optimized processes.
- Ongoing Support and Feedback: Training shouldn’t be a one-time event. Establish channels for ongoing support, such as dedicated help desks or online resources. Encourage feedback from employees to identify any areas where training can be improved or additional support is needed.
Measuring Optimization Success

Process optimization isn’t a “set it and forget it” endeavor. It requires ongoing monitoring and measurement to ensure the changes implemented are delivering the desired results. But how do you measure something as seemingly abstract as “optimization”?
The key is to define concrete, measurable Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that directly align with your optimization goals. These KPIs should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Here are some examples of KPIs you might use to measure optimization success:
- Efficiency: Reduced processing time, decreased error rates, improved resource utilization
- Cost Reduction: Lower operational costs, minimized waste, reduced overtime expenses
- Customer Satisfaction: Increased customer satisfaction scores, reduced complaints, improved Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Quality: Improved product or service quality, decreased defects, reduced rework
- Employee Productivity: Increased output per employee, improved employee satisfaction, reduced turnover
It’s crucial to track these KPIs before, during, and after the optimization process. This allows you to establish a baseline, monitor progress, and demonstrate the tangible impact of your efforts. Regularly analyze the data collected to identify any areas where the optimization efforts have fallen short and to guide further adjustments and refinements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, process optimization is crucial for maximizing business efficiency and boosting overall productivity.