Embark on the journey of building a successful e-commerce business from the ground up with our comprehensive guide. Learn the essential steps and strategies to establish a thriving online store and make your mark in the digital marketplace.
Choosing Your E-Commerce Niche

One of the most critical steps in building a successful e-commerce business is choosing the right niche. Your niche is the specific market segment you’ll target with your products or services. A well-chosen niche can be the difference between struggling to find customers and enjoying a steady stream of targeted traffic.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Niche:
- Passion and Interest: Are you passionate about a particular hobby, industry, or product category? Passion fuels your drive and often translates to a deeper understanding of your target market.
- Market Size and Demand: Is there a large enough audience interested in your niche? Research keywords, analyze trends, and see if there’s existing competition (a good sign!).
- Profitability: Can you source or create products with healthy profit margins? Consider manufacturing costs, shipping fees, and competitor pricing.
- Competition: While some competition is healthy, avoid oversaturated markets where it’s extremely difficult to stand out.
- Scalability: Can your niche grow with your business? Choose a niche with the potential for expansion and new product lines.
Niche Selection Strategies:
- Solve a Problem: Identify a common pain point or problem faced by a specific group of people and offer a product or service as a solution.
- Target a Specific Demographic: Focus on a well-defined demographic group with unique needs and interests, such as eco-conscious consumers or pet owners.
- Capitalize on Trends: Stay ahead of the curve by identifying emerging trends and offering products that cater to those interests.
Take your time researching and evaluating different niches. Don’t be afraid to experiment and adjust your focus as you gain a better understanding of the market. Remember, choosing the right e-commerce niche sets the foundation for your entire business, so choose wisely!
Creating an E-Commerce Business Plan
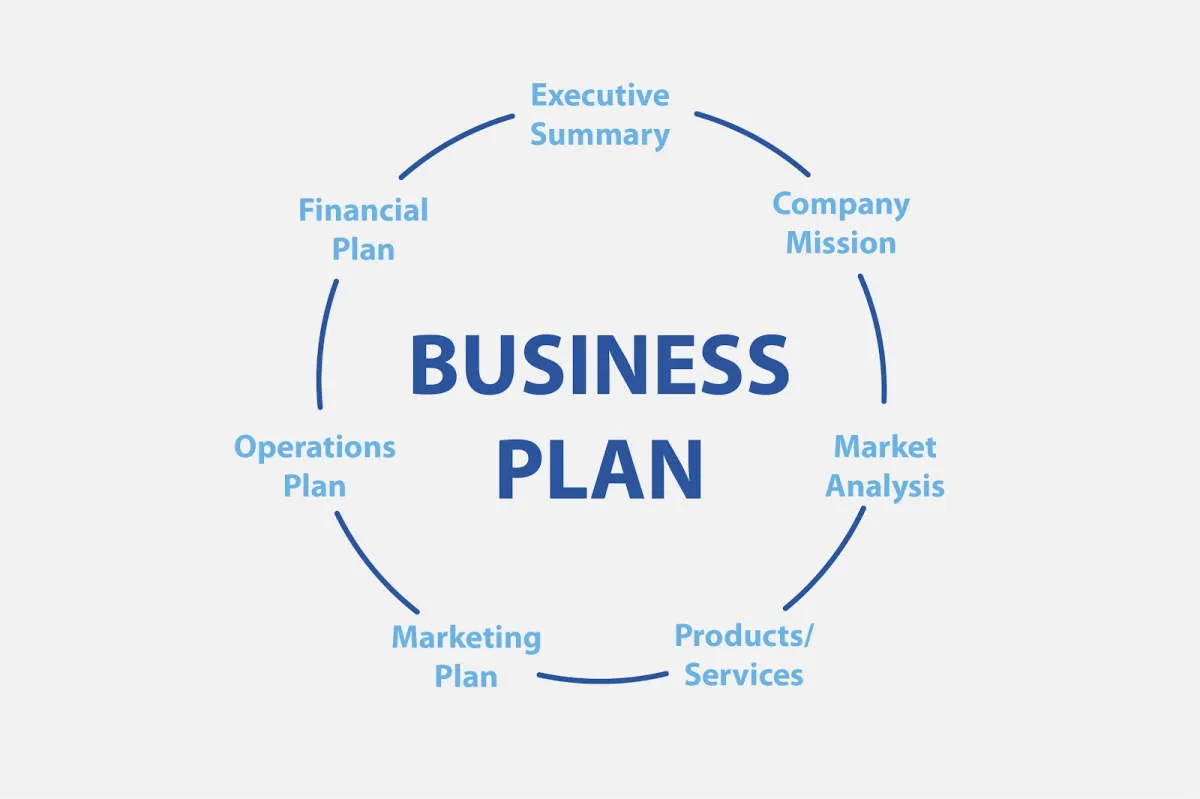
A comprehensive business plan is your roadmap to success in the competitive world of e-commerce. It acts as a blueprint, guiding your decisions and outlining your path to profitability. Here’s a breakdown of what your e-commerce business plan should encompass:
1. Executive Summary
Start with a concise and compelling overview of your business idea. This section should briefly describe your products, target market, competitive advantage, and future goals. Think of it as a snapshot of your business plan designed to capture the reader’s attention.
2. Company Description
Provide a detailed description of your e-commerce business. This should include:
- Business name and legal structure
- Mission statement and core values
- Products or services offered
- Target audience and market analysis
- Competitive landscape and your unique selling proposition (USP)
3. Products or Services
Dive deep into the specifics of what you’re selling. Explain:
- Product descriptions and benefits
- Pricing strategy
- Inventory management plans
- Sourcing and fulfillment processes
4. Marketing and Sales Strategy
Outline how you intend to reach and acquire customers. Your marketing plan should encompass:
- Online marketing: SEO, social media, content marketing, email marketing, paid advertising
- Offline marketing: Print media, events, partnerships (if applicable)
- Sales channels: Your own website, online marketplaces, social commerce platforms
- Customer retention strategies: Loyalty programs, email marketing, personalized offers
5. Operations Plan
Detail the day-to-day operations of your e-commerce business. Address elements such as:
- Website development and platform choice
- Order processing and fulfillment procedures
- Shipping and delivery methods
- Customer service protocols
- Payment gateway integration
6. Management Team
Highlight the key individuals behind your business, showcasing their experience and expertise. Include information on:
- Founders and their roles
- Management structure
- Advisory board members (if applicable)
7. Financial Projections
Provide realistic financial forecasts, including:
- Startup costs
- Projected income statements (revenue and expenses)
- Cash flow statements
- Break-even analysis
- Funding requests (if seeking investment)
8. Appendix
Use this section for any supplementary documents, such as:
- Market research data
- Competitor analysis
- Product images or catalogs
- Legal agreements
Building a User-Friendly Website

A user-friendly website is crucial for the success of any e-commerce business. It should be easy to navigate, visually appealing, and provide a seamless shopping experience. Here are key considerations when building your e-commerce website:
1. Intuitive Navigation and Site Structure
A well-organized website allows customers to find what they need quickly and easily. Implement a clear and logical menu structure, using categories and subcategories to organize products. Include a search bar for quick product searches. Use breadcrumbs to show users their location on the site and help them navigate back easily.
2. Mobile Optimization
With a significant portion of online shopping done on mobile devices, ensure your website is fully responsive. It should adjust seamlessly to different screen sizes, providing a consistent experience across all devices.
3. High-Quality Product Images and Descriptions
Showcase your products with high-resolution images from multiple angles. Write detailed and compelling product descriptions that highlight key features, benefits, and specifications.
4. Secure and Easy Checkout Process
A complicated checkout process is a major reason for cart abandonment. Simplify your checkout process by minimizing the number of steps required. Offer guest checkout options and multiple payment gateways. Ensure your website is secure and displays trust badges to build customer confidence.
5. Fast Loading Speed
Website speed is crucial for user experience. Optimize your website for fast loading times to reduce bounce rates. Compress images, leverage browser caching, and choose a reliable hosting provider.
6. Customer Support and Contact Information
Make it easy for customers to contact you for assistance. Provide clear contact information, including email address, phone number, and a physical address. Consider incorporating a live chat feature for instant support.
Implementing SEO Strategies

Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is crucial for driving organic traffic to your e-commerce website. Here’s how to get started:
Keyword Research
Identify relevant keywords: Conduct thorough keyword research to determine the terms potential customers use to search for products like yours. Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush.
On-Page Optimization
Optimize product pages: Use targeted keywords in product titles, descriptions, image alt tags, and URLs. Write compelling and informative product descriptions.
Improve website structure: Create a clear and logical website hierarchy with categories and subcategories. Ensure easy navigation for both users and search engines.
Content Marketing
Create valuable content: Develop high-quality blog posts, articles, guides, and videos that provide valuable information related to your products or industry. Naturally incorporate relevant keywords.
Technical SEO
Optimize website speed: A fast-loading website improves user experience and search engine rankings. Optimize images, leverage browser caching, and choose a reliable hosting provider.
Ensure mobile-friendliness: With a significant portion of online shopping happening on mobile devices, a responsive website is essential. Test your website’s mobile-friendliness using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
Link Building
Earn backlinks: Acquire high-quality backlinks from reputable websites in your niche. Guest blogging, influencer outreach, and broken link building are effective strategies.
Utilizing Social Media Marketing

Social media is a powerful tool for e-commerce businesses to connect with potential customers, build brand awareness, and drive sales. Here’s how to effectively leverage it:
1. Identify Your Target Audience
Knowing your target audience is crucial. Which platforms do they use most? What are their interests? This information will guide your content strategy and platform selection.
2. Choose the Right Platforms
Don’t spread yourself too thin. Focus on platforms where your target audience is most active. Popular choices for e-commerce include:
- Instagram: Ideal for visually appealing products, lifestyle content, and influencer marketing.
- Facebook: Wide reach, diverse ad targeting options, and the ability to create a shoppable storefront.
- Pinterest: Excellent for driving traffic to your website through visually appealing product pins and inspirational content.
- TikTok: Great for reaching a younger audience with short-form videos, trends, and influencer collaborations.
3. Create Engaging Content
Share a mix of content that resonates with your audience, including:
- High-quality product photos and videos: Showcase your products in the best possible light.
- Behind-the-scenes glimpses: Give your audience a peek into your brand’s story and values.
- User-generated content: Encourage customers to share their experiences with your products.
- Contests and giveaways: Drive engagement and generate excitement.
4. Run Targeted Advertising Campaigns
Social media platforms offer powerful advertising options to reach your ideal customers. Utilize targeting based on demographics, interests, and behaviors to maximize your ad spend.
5. Engage with Your Followers
Respond to comments and messages promptly. Foster a sense of community by asking questions, running polls, and encouraging interaction.
6. Track Your Results and Adjust
Regularly analyze your social media performance using platform analytics. Identify what’s working, what’s not, and make adjustments to your strategy accordingly.
Managing Inventory and Fulfillment
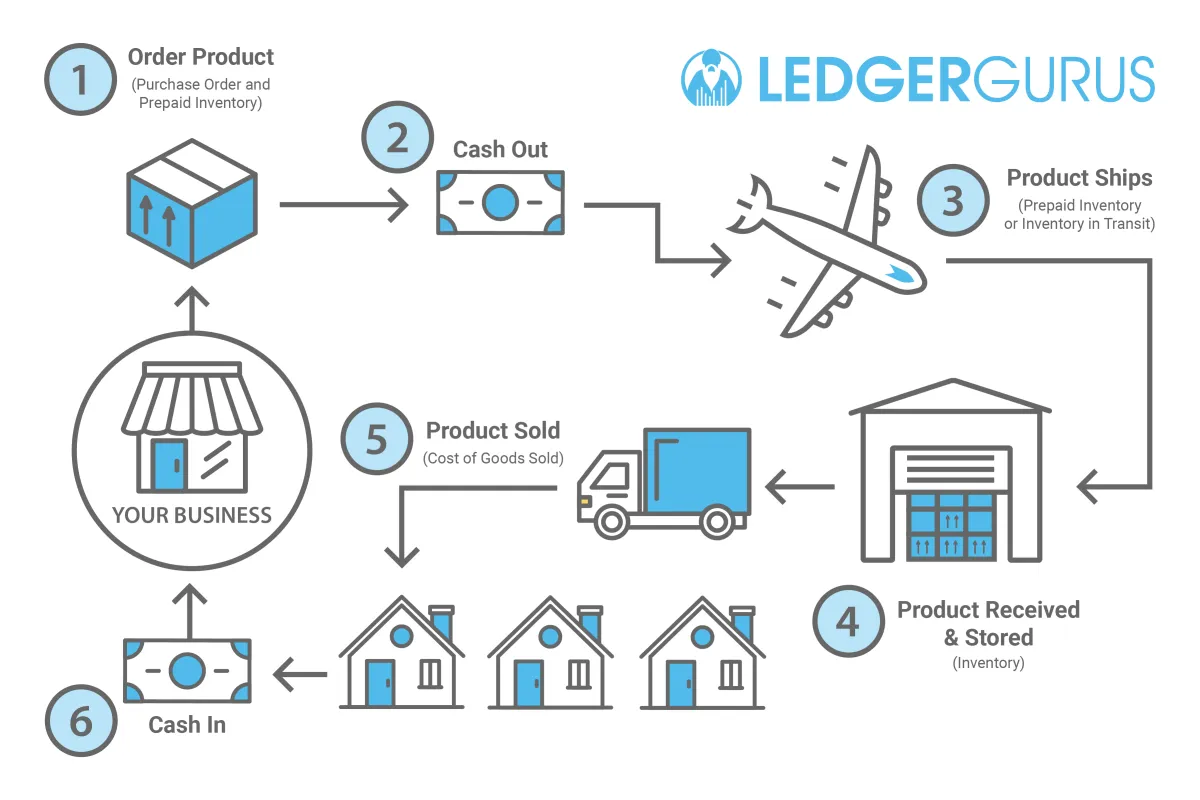
Inventory and fulfillment are the backbone of your e-commerce operation. Mismanagement in these areas can lead to lost sales, unhappy customers, and ultimately, a failing business. Here’s how to effectively manage inventory and fulfillment:
1. Choose the Right Inventory Management System
An inventory management system tracks inventory levels, orders, sales, and deliveries. This helps you make informed decisions about ordering, pricing, and marketing. You can opt for:
- Manual Systems: Suitable for very small businesses with limited products.
- Spreadsheet Software: Affordable option for small businesses starting out.
- Inventory Management Software: Ideal for growing businesses with a wider product range, offering features like automated reordering and sales tracking.
2. Determine Your Inventory Model
Consider these common inventory models:
- Dropshipping: You don’t hold inventory; a third-party handles storage and shipping.
- Self-fulfillment: You store and ship orders yourself, giving you maximum control over the customer experience.
- Third-Party Logistics (3PL): A 3PL provider handles warehousing, packing, and shipping, allowing you to scale efficiently.
Each model has pros and cons related to cost, control, and scalability. Choose one that aligns with your business needs and resources.
3. Optimize Inventory Levels
Avoid stockouts and overstocking by:
- Forecasting Demand: Analyze historical sales data, market trends, and seasonality to predict future demand.
- Setting Reorder Points: Determine the minimum stock level for each product that triggers a new order.
- Monitoring Lead Times: Factor in the time it takes to receive new stock from suppliers.
4. Streamline Order Fulfillment
Efficient order fulfillment ensures timely delivery and customer satisfaction:
- Use Order Management Software: Automate order processing, tracking, and communication with customers.
- Choose Reliable Shipping Partners: Partner with shipping carriers offering competitive rates, reliable service, and tracking capabilities.
- Optimize Packaging: Use appropriate packaging to minimize shipping costs and prevent damage during transit.
5. Track Key Metrics
Regularly monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) to identify areas for improvement. Important metrics include:
- Inventory Turnover Rate
- Order Fulfillment Rate
- Shipping Costs
- Customer Returns Rate
Conclusion
In conclusion, starting a successful e-commerce business requires strategic planning, market research, and continuous adaptation to customer needs. With dedication and innovation, anyone can build a thriving online store from scratch.

