Effective risk management is crucial for the success of any business. Explore essential strategies and tips to minimize risks and maximize opportunities in this comprehensive guide.
Understanding Business Risks
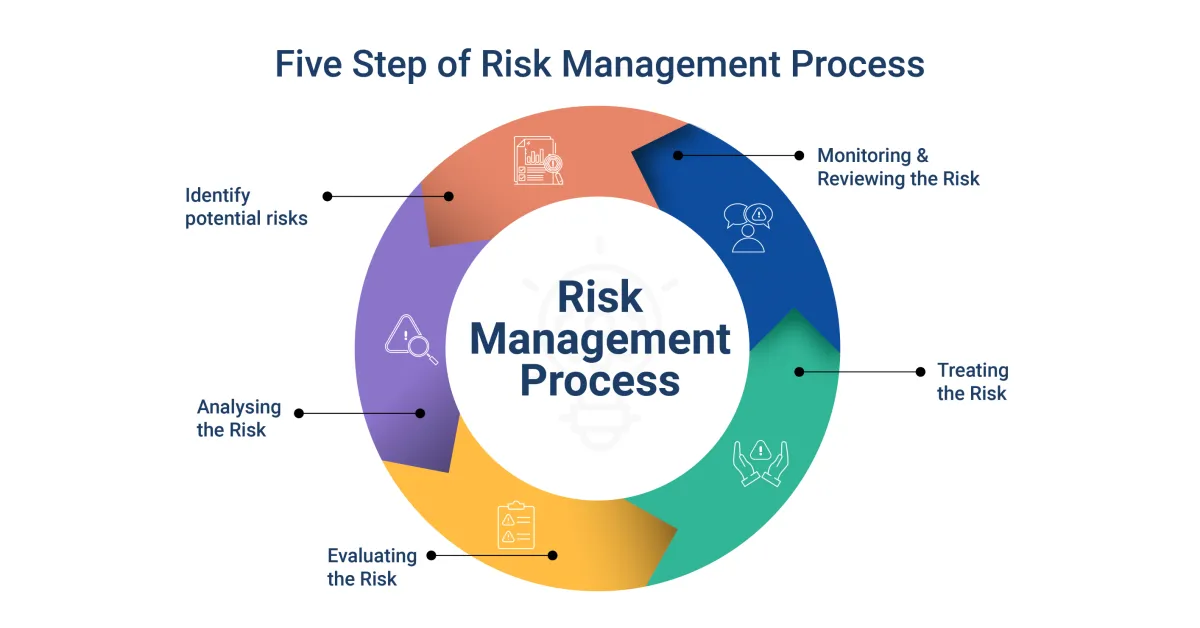
Effective risk management starts with a thorough understanding of the potential risks your business faces. This involves identifying, analyzing, and categorizing these risks to effectively prioritize and mitigate them. Here’s a closer look at the process:
1. Identifying Potential Risks
Begin by brainstorming potential threats to your business operations, finances, reputation, and compliance. Consider both internal risks (e.g., employee errors, data breaches) and external risks (e.g., market fluctuations, natural disasters). Some common categories of business risk include:
- Strategic Risks: Threats to your business model, competitive landscape, or long-term goals.
- Operational Risks: Disruptions to your day-to-day business activities, such as supply chain issues, IT failures, or fraud.
- Financial Risks: Potential losses related to credit, liquidity, market volatility, or interest rate fluctuations.
- Compliance Risks: Violations of laws, regulations, or industry standards.
- Reputational Risks: Damage to your brand image or customer trust due to negative publicity, product recalls, or ethical concerns.
2. Analyzing Risks
Once you’ve identified potential risks, assess them based on two key factors:
- Likelihood: How probable is it that the risk will occur?
- Impact: How severe would the consequences be if the risk materializes?
A risk matrix can be a valuable tool for visualizing and prioritizing risks based on their likelihood and potential impact.
3. Categorizing Risks
Categorizing risks can help you develop targeted risk management strategies. Common categories include:
- Avoidable Risks: Risks that you can completely eliminate by changing business practices or avoiding certain activities.
- Mitigable Risks: Risks that cannot be entirely avoided but can be minimized through preventative measures and controls.
- Transferable Risks: Risks that can be shifted to a third party, such as through insurance or outsourcing.
- Acceptable Risks: Low-impact risks that you decide to accept and monitor, rather than actively mitigating.
Identifying Potential Risks
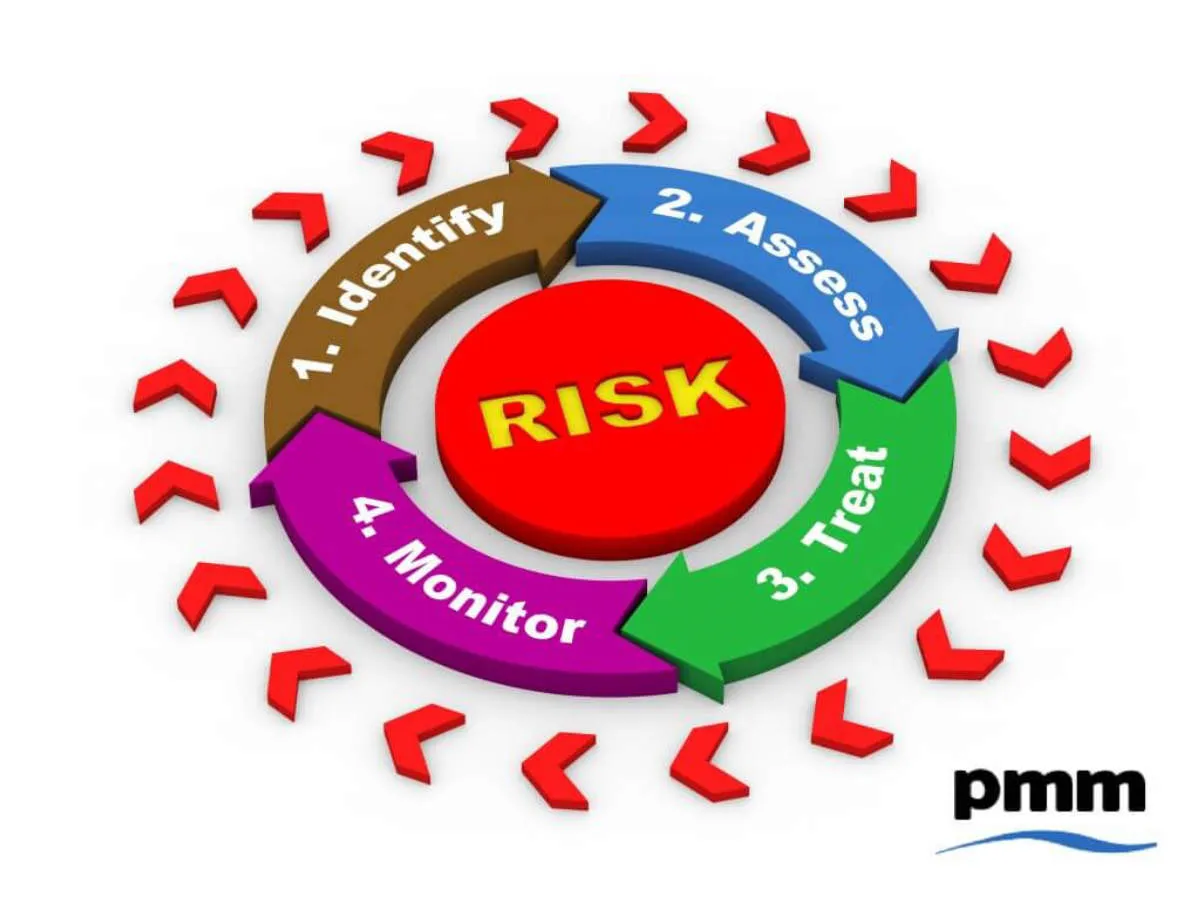
The first step in effective risk management is identifying potential risks that could affect your business. This requires a thorough understanding of your business operations, the industry you operate in, and the broader economic and political landscape. Here are some key areas to consider:
Internal Risks
- Operational risks: These arise from internal processes, systems, or human error. Examples include equipment failure, supply chain disruptions, data breaches, or employee misconduct.
- Financial risks: These relate to the financial health and stability of your business. Examples include cash flow problems, bad debt, currency fluctuations, or interest rate changes.
- Strategic risks: These stem from decisions made at a high level within the organization and impact the overall direction of the business. Examples include poor strategic planning, mergers and acquisitions, or entering new markets.
- Compliance risks: These arise from the need to comply with laws, regulations, and industry standards. Examples include environmental regulations, data protection laws, or health and safety regulations.
External Risks
- Economic risks: These are driven by factors in the broader economy. Examples include recessions, inflation, changes in consumer spending, or global economic instability.
- Political risks: These arise from political events or changes in government policy. Examples include changes in tax law, trade restrictions, or political instability in a key market.
- Environmental risks: These relate to environmental factors that can impact your business. Examples include natural disasters, climate change, or resource scarcity.
- Technological risks: These arise from the rapid pace of technological change. Examples include cybersecurity threats, data breaches, or the emergence of disruptive technologies.
- Reputation risks: These arise from events or actions that could damage your company’s reputation. Examples include negative media coverage, product recalls, or social media crises.
Identifying potential risks is an ongoing process. Regularly review and update your risk assessments to account for changes in your business and the external environment.
Creating a Risk Management Plan
A well-structured risk management plan is the cornerstone of any successful risk management strategy. This plan serves as a roadmap for identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks that could hinder your business objectives.
Steps to Developing a Risk Management Plan:
-
1. Risk Identification:
Start by brainstorming potential risks across all areas of your business. Involve stakeholders from various departments to gather diverse perspectives. Risks can stem from internal factors (e.g., operational inefficiencies, employee errors) or external factors (e.g., market fluctuations, regulatory changes, natural disasters).
-
2. Risk Assessment:
Analyze each identified risk based on its likelihood of occurrence and potential impact on your business. Use a qualitative (e.g., high, medium, low) or quantitative (e.g., numerical scales) approach to prioritize risks effectively. This step helps you focus resources on mitigating the most critical risks.
-
3. Risk Response Planning:
Develop strategies to address each prioritized risk. Common risk responses include:
- Risk Avoidance: Choosing to avoid activities that carry the risk.
- Risk Mitigation: Implementing controls to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk.
- Risk Transfer: Shifting the financial burden of a risk to a third party (e.g., insurance).
- Risk Acceptance: Acknowledging and accepting the risk without taking action, usually for risks with low potential impact.
-
4. Risk Monitoring and Review:
A risk management plan is not static; it requires continuous monitoring and periodic review. Track the effectiveness of your risk mitigation strategies and make adjustments as needed. Regularly assess for new or evolving risks, especially in response to internal or external changes.
Implementing Risk Mitigation Strategies
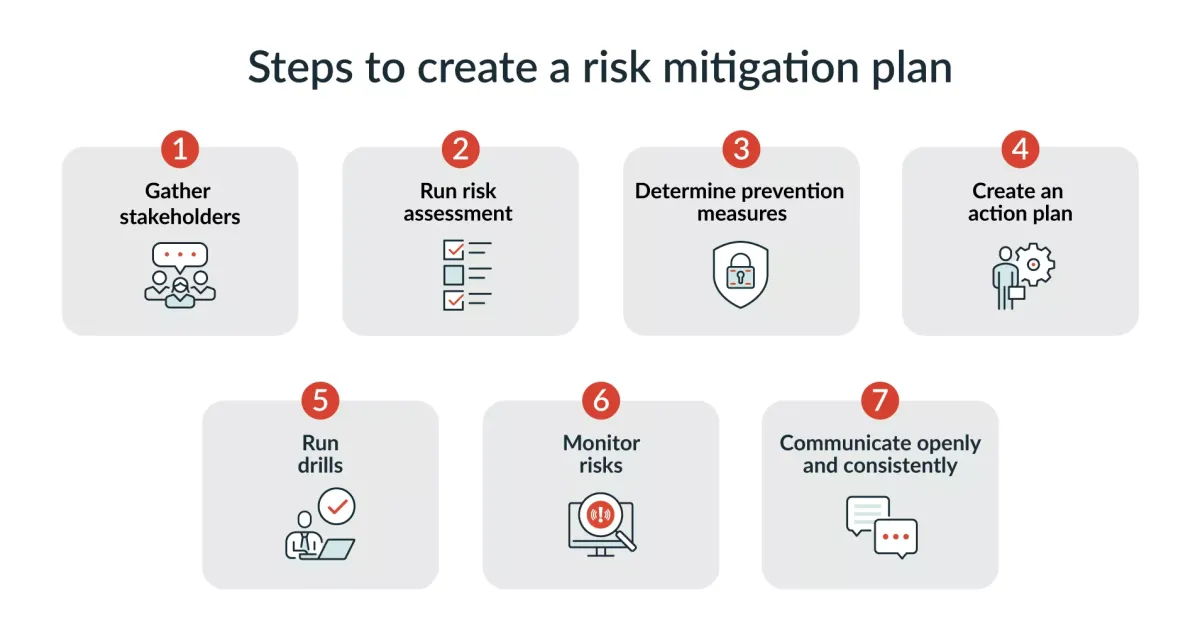
Once you’ve identified and analyzed potential risks, the next crucial step is to develop and implement strategies to mitigate them. This involves choosing actions that minimize the likelihood or impact of these risks. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
1. Prioritize Risks:
Not all risks are created equal. Prioritize risks based on their potential impact and likelihood. Focus on mitigating the most critical risks first.
2. Choose Mitigation Strategies:
There are several risk mitigation strategies, and the best choice often depends on the specific risk. Common strategies include:
- Risk Avoidance: Completely avoiding the activity or decision that creates the risk.
- Risk Reduction: Taking steps to decrease the likelihood or impact of the risk.
- Risk Transfer: Shifting the risk to a third party, such as through insurance or outsourcing.
- Risk Acceptance: Acknowledging the risk and its potential impact but choosing to accept it, often for low-impact risks.
3. Develop Action Plans:
For each chosen strategy, create a detailed action plan. Clearly outline the steps to be taken, responsibilities, deadlines, and resources required.
4. Implement and Communicate:
Put the action plans into action. Communicate the strategies and action plans to relevant stakeholders within the organization, ensuring everyone understands their roles and responsibilities.
5. Monitor and Review:
Implementing mitigation strategies is not a one-time task. Continuously monitor the effectiveness of these strategies, making adjustments as needed. Regularly review your risk assessments and mitigation plans to adapt to changes in the business environment or as new risks emerge.
Monitoring and Reviewing Risks

Risk management isn’t a “set it and forget it” process. The business environment is constantly changing, meaning identified risks can evolve and new risks can emerge. Monitoring and reviewing risks is essential to ensure your risk management strategies remain effective and relevant.
This ongoing process typically involves:
- Regularly reviewing identified risks: Assess if the likelihood or impact of each risk has changed, and if existing control measures are still adequate.
- Identifying new risks: Market shifts, technological advancements, and even internal organizational changes can introduce new risks. Continuous monitoring helps you stay ahead of these.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of risk controls: Analyze if your risk mitigation strategies are working as intended. Are they effectively reducing the likelihood or impact of risks?
- Making necessary adjustments: Based on your monitoring and review, adapt your risk management plan. This might involve revising existing controls, implementing new ones, or even reconsidering your overall risk appetite.
The frequency of your reviews will depend on the nature of your business and the volatility of your industry. Some businesses may benefit from quarterly reviews, while others might need more frequent assessments.
Adapting to Changes

The business landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies, regulations, and market trends emerging regularly. Effective risk management requires a flexible and adaptable approach that can keep pace with these changes.
Here are key strategies for adapting to changes in the context of risk management:
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement systems to track internal and external changes that could impact your risk profile. This could involve monitoring news sources, industry publications, regulatory updates, and competitor activities.
- Regular Risk Reassessments: Don’t treat your initial risk assessment as static. Regularly review and update your risk assessments to reflect new information, changing circumstances, and lessons learned from past incidents.
- Scenario Planning: Develop contingency plans for various potential scenarios, including unexpected events or disruptions. This helps your business be prepared to respond effectively to unforeseen challenges.
- Agile Decision-Making: Foster a culture of agility and adaptability within your organization. Encourage employees at all levels to be proactive in identifying potential risks and proposing solutions.
- Embrace Technology: Leverage technology to enhance your risk management capabilities. Utilize data analytics, risk management software, and other tools to improve risk identification, assessment, and monitoring processes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, implementing proactive risk management strategies is vital for business success and sustainability.

